
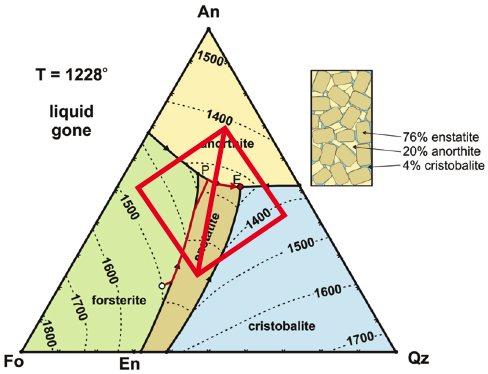
A completely glassy texture is called holohyaline texture. The resulting texture will be glassy, with a few tiny crystals called microlites.
Thus few crystals will form and they will not grow to any large size. If the size of the grains are so small that crystals cannot be distinguished with a hand lens, the texture is said to be aphanitic.Īt high degrees of undercooling, both the growth rate and nucleation rate will be low. This will result in many crystals all growing rapidly, but because there are so many crystals, they will run into each other before they have time to grow and the resulting texture will be a fine grained texture. Note that the rate of crystal growth and nucleation depends on how long the magma resides at a specified degree of undercooling (DT = Tm - T), and thus the rate at which temperature is lowered below the the crystallization temperature.Īt larger degrees of undercooling, the nucleation rate will be high and the growth rate also high. Shown below are hypothetical nucleation and growth rate curves based on experiments in simple systems. First, nucleation and growth cannot occur until temperatures are below the temperature at which equilibrium crystallization begins. The crystal can then grow until it runs into other crystals or the supply of chemical constituents is cut off.Īll of these rates are strongly dependent on the temperature of the system. Once a nucleus forms, the chemical constituents must diffuse through the liquid to arrive at the surface of the growing crystal. In order for a crystal to form in a magma enough of the chemical constituents that will make up the crystal must be at the same place at the same time to form a nucleus of the crystal. This depends largely on the diffusion rate of the molecules of concern. The rate of growth of crystals - the rate at which new constituents can arrive at the surface of the growing crystal.The rate of nucleation of new crystals - the rate at which enough of the chemical constituents of a crystal can come together in one place without dissolving.The diffusion rate - the rate at which atoms or molecules can move (diffuse) through th liquid.The main factor that determines the texture of an igneous rock is the cooling rate (dT/dt). Extrusive rocks are usually distinguished from intrusive rocks on the basis of their texture and mineral composition. By contrast, intrusive rocks are formed from magma that was forced into older rocks at depth within the Earth’s crust the molten material then slowly solidifies below the Earth’s surface, where it may later be exposed through erosion. Extrusive rock, any rock derived from magma (molten silicate material) that was poured out or ejected at the Earth’s surface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
